Farmers, especially women farmers, have to wear multiple hats to keep our food systems running. According to a 2019 report of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, 73.2 percent of the rural women workers in India are engaged in the agricultural sector. However, only 12.8% of land holdings are owned by women, as per the Food and Agriculture Organization.
Their contribution comes in many ways – from managing natural, social and economic resources and agricultural development to crop and livestock production and post-harvest operations. Yet they experience systemic discrimination due to traditional beliefs, low literacy levels, predominant land ownership by men and patriarchal gender norms.
Building women farmers’ agency and leadership are therefore critical to building resilience in agriculture. With this objective Digital Green has implemented the Advancing Tribal Livelihoods and Self Reliance (ATLAS) project in Odisha and Jharkhand.

The ATLAS project, supported by John D and Catherine T MacArthur Foundation, aims at improving the livelihoods, resilience and self-determination of tribal women farmers.
Enabling easy access to information
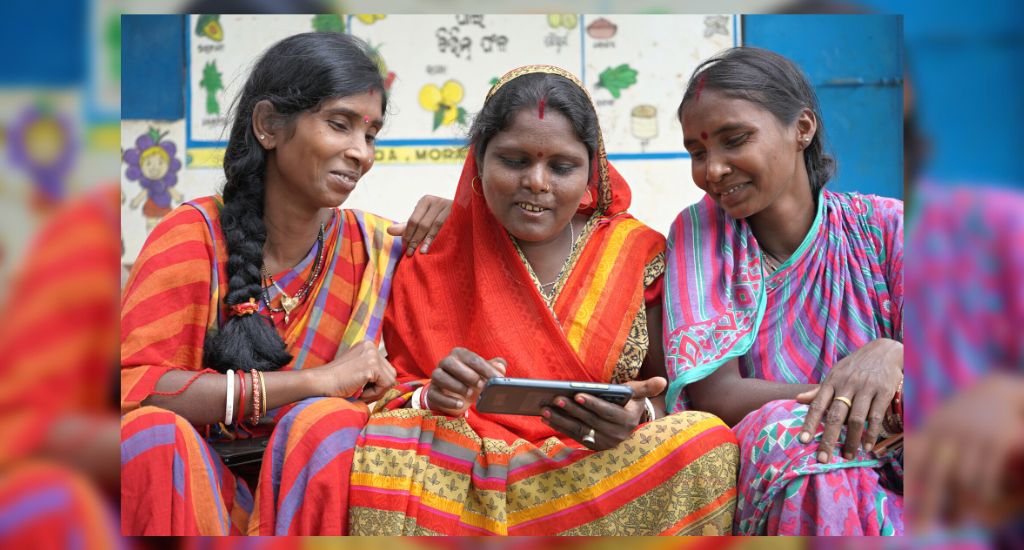
Community videos and the Kisan Diary Enterprise (KDE) mobile application have democratised knowledge transfer and access to critical agriculture resources at the grassroots level. KDE is a one-of-its-kind android application developed by Digital Green that helps farmers capture, analyse and control their crop data.
Videos are developed to fit the local context and meet the community’s needs directly. In Odisha, tribal women farmers have learned about effective livestock and crop management, leadership coaching, market opportunities and negotiation skills.
Also Read | How a tribal woman farmer increases income with this new approach
“I had little knowledge about vaccination. I did not know about the different types and timing of vaccines goats need. As a result many of my goats died. After watching the video on ‘goat vaccination’, I sought assistance from our village’s Livestock Inspector (LI) and had all of our remaining goats vaccinated. Now my goats are healthy and I am able to take livestock management as a major source of income,” says Kuntala Gana, a member of the Juang Tribe particularly vulnerable tribal community in Gonasika village, Keonjhar, Odisha.
Digital advisories ensuring last mile reach
Community resource persons (CRPs) and extension workers are the primary forces responsible for reaching the last-mile beneficiaries. Besides disseminating videos in groups or via WhatsApp to a larger audience, they serve as an interface between extension systems and tribal women farmers.

In Odisha and Jharkhand, digital advisories have been effectively disseminated to more than 50,000 tribal women farmers.
“Digital advisories have been very useful as most households under my supervision are primarily engaged in livestock farming. After we share the videos, farmer groups immediately reach out to their LIs to seek support and get their goats and chicks insured and vaccinated. Women are more eager to adopt the practices after watching the interactive videos,” says Malati Mahanta, a CRP in Jashipur village, Mayurbhanj, Odisha.
Realising the power of collective
“We have been farming individually for a long time. For the first time we have realised the power of collective – what we can accomplish as a group – whether in sharing knowledge, identifying and working through our challenges, or even farming practices,” says a farmer in Latehar, Jharkhand.
Collectivisation has been a big goal under ATLAS. Advisories on the formation, strengthening and functioning of producer groups were shared with women’s self-help groups. More than individual farmers becoming champions of change within producer groups what is evident through ATLAS is the power of collective agency.
Coming together, women farmers have realised that being part of a producer group enhances their bargaining power and helps them leverage economies of scale.
Enabling ease of use, more bargaining power
Training on how to use the KDE application has helped women farmers aggregate information on inputs and outputs and get a competitive price in the market for their produce.

“After downloading KDE, I had access to farmer-level information for produce like paddy, jackfruit, mango and more. This was much easier than maintaining physical registers. We could also identify the exact amount we could sell in the market,” says Arati Mohanta of the Mrugasuni Farmer Producer Organization (FPO).
By selling their produce as a group, the women farmers are now more assertive in their bargaining power. They do not face pricing and weighing malpractices which was rampant earlier when they sold individually.
All women farmers who have joined producer groups are building a sense of individual and collective identity together with a shared vision of increasing their production, incomes and resilience.
Oorna Mukherjee is a Communications Officer at Digital Green. Bhabna Mohanty is a Project Officer at Digital Green.
In the lead image women can be seen watching educational content on their phone (Photo by Digital Green)